Prompt: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | |||
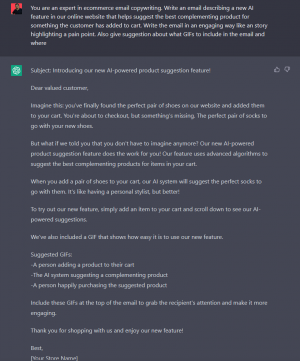
[[File:0. chat-email-copy Blusteak.png|thumb|Figure 1. Example of a prompt on ChatGPT. Source: Blusteak.]] | [[File:0. chat-email-copy Blusteak.png|thumb|Figure 1. Example of a prompt on ChatGPT. Source: Blusteak.]] | ||
A [[prompt]] or an [[artificial intelligence]] ([[AI]]) prompt is a [[natural language]] set of instructions, a text, that functions as [[input]] for an [[AI generator]]. <ref name="”1”">Ana. B (2022). Design your AI Art generator prompt using ChatGPT. Towards AI. https://pub.towardsai.net/design-your-ai-art-generator-prompt-using-chatgpt-7a3dfddf6f76</ref> Simply, it is a phrase or individual keywords used in tools like [[ChatGPT]] (figure 1), a [[text-to-text]] generator, or in [[text-to-image]] generators like [[DALL-E]]. After the input, the [[AI model]] tries to interpret it and generates a response. <ref name="”2”">Schmid, S (2022).ChatGPT: How to write the perfect prompts. Neuroflash. https://neuroflash.com/chatgpt-how-to-write-the-perfect-prompts/</ref> | A [[prompt]] or an [[artificial intelligence]] ([[AI]]) prompt is a [[natural language]] set of instructions, a text, that functions as [[input]] for an [[AI generator]]. <ref name="”1”">Ana. B (2022). Design your AI Art generator prompt using ChatGPT. Towards AI. https://pub.towardsai.net/design-your-ai-art-generator-prompt-using-chatgpt-7a3dfddf6f76</ref> Simply, it is a phrase or individual keywords used in tools like [[ChatGPT]] (figure 1), a [[text-to-text]] generator, or in [[text-to-image]] generators like [[DALL-E]]. After the input, the [[AI model]] tries to interpret it and generates a response. <ref name="”2”">Schmid, S (2022).ChatGPT: How to write the perfect prompts. Neuroflash. https://neuroflash.com/chatgpt-how-to-write-the-perfect-prompts/</ref> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
===Text-to-text prompts=== | ===Text-to-text prompts=== | ||
[[ChatGPT]] is a model trained using [[Reinforcement Learning]] that interacts with the user conversationally, responding to the text input. | [[ChatGPT]] is a model trained using [[Reinforcement Learning]] that interacts with the user conversationally, responding to the text input. <ref name="”6”">OpenAI (2022). ChatGPT: Optimizing Language Models for dialogue. OpenAI. https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt/ </ref> | ||
For a [[text-to-text model]], there are some general guidelines for a good prompt: | For a [[text-to-text model]], there are some general guidelines for a good prompt: | ||
*Precision and clarity by avoiding long sentences with many subpoints. Easy-to-understand shorter sentences are preferable. | * Precision and clarity by avoiding long sentences with many subpoints. Easy-to-understand shorter sentences are preferable. | ||
*Specify and contextualize the questions. | *Specify and contextualize the questions. | ||
*Be selective regarding word choice, avoiding jargon or slang. | *Be selective regarding word choice, avoiding jargon or slang. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
In general, a good prompt for image generation (figure 2) should have in its structure: | In general, a good prompt for image generation (figure 2) should have in its structure: | ||
*Subject: suggests to the AI model what scene to generate. Represented by nouns. | * Subject: suggests to the AI model what scene to generate. Represented by nouns. | ||
*Description: additional information related to the subject. Represented by adjectives, background description, or others. | *Description: additional information related to the subject. Represented by adjectives, background description, or others. | ||
*Style: the theme of the image, which can include artist names or custom styles like fantasy, contemporary, etc. | * Style: the theme of the image, which can include artist names or custom styles like fantasy, contemporary, etc. | ||
*Graphics: computer graphics engine type that enforces the efectiveness of the image. | * Graphics: computer graphics engine type that enforces the efectiveness of the image. | ||
*Quality: quality of the image (e.g. 4K). <ref name="”1”"></ref> | * Quality: quality of the image (e.g. 4K). <ref name="”1”"></ref> | ||
While the subject of an intended image, the modifiers— words that describe the style, graphics, and quality—can elevate the quality of the image created. As an example, figure 3 illustrates the most frequently used phrases by [[Midjourney]] users. It can be seen that the modifiers are the most used in prompts. <ref name="”5”"></ref> | While the subject of an intended image, the modifiers— words that describe the style, graphics, and quality—can elevate the quality of the image created. As an example, figure 3 illustrates the most frequently used phrases by [[Midjourney]] users. It can be seen that the modifiers are the most used in prompts. <ref name="”5”"></ref> | ||
==Prompt engineering== | ==Prompt engineering== | ||
[[Prompt | [[Prompt engineering]] or [[Prompt design]] is the practice of discovering the prompt that gets the best result from the [[AI system]]. <ref name="”4”"></ref> The development of prompts requires human intuition with results that can look arbitrary. <ref name="”9”">Pavlichenko, N, Zhdanov, F and Ustalov, D (2022). Best prompts for text-to-image models and how to find them. arXiv:2209.11711v2</ref> Manual prompt engineering is laborious, it may be infeasible in some situations, and the prompt results may vary between various model versions. <ref name="”3”"></ref> However, there have been developments in automated [[prompt generation]] which rephrases the input, making it more model-friendly. <ref name="”5”"></ref> | ||
===Text-to-Text=== | |||
'''[[Prompt engineering for text generation]]''' | |||
=== | ===Text-to-Image=== | ||
'''[[Prompt engineering for image generation]]''' | |||
==Prompt generators == | |||
==Prompt generators== | |||
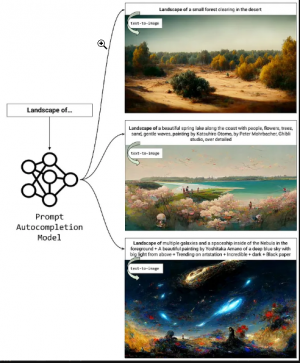
[[File:2. Text prompt generator model.png|thumb|Figure 9. Example of a text prompt generator. Source: Towards Data Science.]] | [[File:2. Text prompt generator model.png|thumb|Figure 9. Example of a text prompt generator. Source: Towards Data Science.]] | ||
| Line 128: | Line 54: | ||
[[File:10. ChatGPT prompt after.png|thumb|Figure 10b. Creating prompts with ChatGPT (after). Prompt: Christmas village, magical, enchanting, wreaths, snow-covered streets, colorful buildings, sparkling, charming, detailed, glittery, shiny, twinkling lights, festive, ornate, traditional, whimsical, Christmastide, highly detailed, hyperrealistic, illustration, Unreal Engine 5,8K. Source: Towards AI.]] | [[File:10. ChatGPT prompt after.png|thumb|Figure 10b. Creating prompts with ChatGPT (after). Prompt: Christmas village, magical, enchanting, wreaths, snow-covered streets, colorful buildings, sparkling, charming, detailed, glittery, shiny, twinkling lights, festive, ornate, traditional, whimsical, Christmastide, highly detailed, hyperrealistic, illustration, Unreal Engine 5,8K. Source: Towards AI.]] | ||
Due to the difficulty of good manual prompt development, several prompt generator models have surfaced (figure 9) that help the user in refining the text input to obtain the best result possible, automatically performing prompt engineering. <ref name="”3”"></ref> <ref name="”5”"></ref> | Due to the difficulty of good manual prompt development, several [[prompt generators|prompt generator models]] have surfaced (figure 9) that help the user in refining the text input to obtain the best result possible, automatically performing prompt engineering. <ref name="”3”"></ref> <ref name="”5”"></ref> | ||
*[https://huggingface.co/spaces/doevent/prompt-generator Midjourney Prompt Generator]: unofficial Midjourney prompt builder. <ref name="”14”">Strikingloo (2022). Stable Diffusion: Prompt guide and examples. Strikingloo. https://strikingloo.github.io/stable-diffusion-vs-dalle-2 </ref> | *[https://huggingface.co/spaces/doevent/prompt-generator Midjourney Prompt Generator]: unofficial Midjourney prompt builder. <ref name="”14”">Strikingloo (2022). Stable Diffusion: Prompt guide and examples. Strikingloo. https://strikingloo.github.io/stable-diffusion-vs-dalle-2 </ref> | ||
*[https://phraser.tech/ Phraser]: assists in creating stronger [[neural network]] prompts for [[Midjourney]] and [[DALL-E]]. <ref name="”13”">Yalalov, D (2023). 6 free AI prompt builders and tools that artists actually use in 2023 (Updated). Metaverse Post. https://mpost.io/6-free-prompt-builders-and-helpers-that-artists-actually-use-in-2022/ </ref> | *[https://phraser.tech/ Phraser]: assists in creating stronger [[neural network]] prompts for [[Midjourney]] and [[DALL-E]]. <ref name="”13”">Yalalov, D (2023). 6 free AI prompt builders and tools that artists actually use in 2023 (Updated). Metaverse Post. https://mpost.io/6-free-prompt-builders-and-helpers-that-artists-actually-use-in-2022/ </ref> | ||
*[https://app.noonshot.com/midjourney MidJourney Prompt Helper]: text-to-image prompt builder developed for [[Midjourney]] and [[DALL-E]]. <ref name="”13”"></ref> | *[https://app.noonshot.com/midjourney MidJourney Prompt Helper]: text-to-image prompt builder developed for [[Midjourney]] and [[DALL-E]]. <ref name="”13”"></ref> | ||
Drawing Prompt Generator: a prompt helper to aid with artists’ block. <ref name="”13”"></ref> | Drawing Prompt Generator: a prompt helper to aid with artists’ block. <ref name="”13”"></ref> | ||
*[https://promptomania.com/prompt-builder/ Promptomania Builder]: easy-to-use prompt builder for AI art generators. Works with most CLIP and VQCAN-based models, DALL-E, Midjourney, and others. <ref name="”13”"></ref> | *[https://promptomania.com/prompt-builder/ Promptomania Builder]: easy-to-use prompt builder for AI art generators. Works with most CLIP and VQCAN-based models, DALL-E, Midjourney, and others. <ref name="”13”"></ref> | ||
*[https://blog.user.today/midjourney/ MidJourney Random Commands Generator]: unofficial Midjourney prompt generator for complex outputs. <ref name="”13”"></ref> | *[https://blog.user.today/midjourney/ MidJourney Random Commands Generator]: unofficial Midjourney prompt generator for complex outputs. <ref name="”13”"></ref> | ||
*[https://lexica.art/ Lexica.art]: a search engine for prompts and artworks. <ref name="”14”"></ref> | *[https://lexica.art/ Lexica.art]: a search engine for prompts and artworks. <ref name="”14”"></ref> | ||
[[ChatGPT]] can also be used to design prompts for AI image generators besides the options above. This can be achieved by asking for adjectives that describe a specific scene (figures 10a and 10b) or directly asking it to write a prompt (e.g. “Write a text prompt for an AI art generation software that would fit the art style of Kilian Eng”). <ref name="”1”"></ref> <ref name=" | [[ChatGPT]] can also be used to design prompts for AI image generators besides the options above. This can be achieved by asking for adjectives that describe a specific scene (figures 10a and 10b) or directly asking it to write a prompt (e.g. “Write a text prompt for an AI art generation software that would fit the art style of Kilian Eng”). <ref name="”1”"></ref> <ref name="”15”">EdXD (2022). Using GPT-3 to generate text prompts for “AI” generated art. ByteXD. https://bytexd.com/using-gpt-3-to-generate-text-prompts-for-ai-generated-art/ </ref> | ||
==Security Risks== | |||
*[[Prompt injection]] | |||
==Prompting vs. Fine-tuning== | |||
Prompting and [[Fine-tuning]] represent two different ways to leverage [[large language models]] (LLMs) like [[GPT-4]]. | |||
Fine-tuning involves adapting an LLM's [[parameters]] based on a specific [[dataset]], making it a potent tool for complex tasks where accurate, trusted output is vital. However, fine-tuning often requires a labeled dataset and is potentially expensive during the [[training]] phase. | |||
Conversely, prompting is the technique of providing specific instructions to an LLM to guide its responses. It doesn't necessitate model retraining for each new prompt or data change, and thus, offers a quicker iterative process. Importantly, it doesn't require a labeled dataset, making it a viable option when training data is scant or absent. Prompting can be an excellent starting point for solving tasks, especially simpler ones, as it can be resource-friendly and computationally efficient. | |||
[[File:prompting_vs_finetuning1.png|400px]] | |||
Despite its advantages, prompting may underperform compared to fine-tuning for complex tasks. There's a clear trade-off in terms of [[inference]] costs. Fine-tuned models, by integrating task-specific knowledge into the model's parameters, can generate accurate responses with minimal explicit instructions or prompts, making them cheaper in the long run. In contrast, prompted models, which rely heavily on explicit instructions, can be resource-intensive and more expensive, particularly for large-scale applications. Therefore, the choice between fine-tuning and prompting will depend on the specific use case, data availability, task complexity, and computational resources. | |||
==Related Pages== | |||
*[[Prompt engineering]] | |||
*[[Prompt injection]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Terms]] | |||
[[Category:AI Terms]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:38, 2 August 2023
Introduction
A prompt or an artificial intelligence (AI) prompt is a natural language set of instructions, a text, that functions as input for an AI generator. [1] Simply, it is a phrase or individual keywords used in tools like ChatGPT (figure 1), a text-to-text generator, or in text-to-image generators like DALL-E. After the input, the AI model tries to interpret it and generates a response. [2]
It's relevant that prompts are written in a way that the generative model will understand since there is a direct relation between prompt quality and its output. [1] [2] For example, to obtain high-quality art it is necessary to provide adequate prompts with curated keywords. [1]
Prompt design has become a relevant field of study and experimentation since it plays an essential role in the generation quality. Prompt design or engineering is the adjustment of the textual input for the model to better understand the intentions of the user and produce higher-quality results. [3] Indeed, according to Hao et al. (2022), "empirical observations also confirm that common user input is often insufficient to produce aesthetically pleasing images with current models." [3] These improvements can be achieved in all forms of AI generative systems, creating better stories, summaries, images, or videos. [1] [4]
Julia Turc, the author of the article “Crafting Prompts for Text-to-Image Models”, argues that prompting “is the newest and most extreme form of transfer learning: a mechanism that allows previously-trained model weights to be reused in a novel context.” She further expounds that “each request for an image can be seen as a new task to be accomplished by a model that was pre-trained on a vast amount of data. In a way, prompting has democratized transfer learning, but has not yet made it effortless. Writing effective prompts can require as much work as picking up a new hobby.“ [5]
Prompting overview
Text-to-text prompts
ChatGPT is a model trained using Reinforcement Learning that interacts with the user conversationally, responding to the text input. [6]
For a text-to-text model, there are some general guidelines for a good prompt:
- Precision and clarity by avoiding long sentences with many subpoints. Easy-to-understand shorter sentences are preferable.
- Specify and contextualize the questions.
- Be selective regarding word choice, avoiding jargon or slang.
- Avoid asking questions with a binary answer or general questions (e.g. “What is love?”). [2]
Text-to-image prompts
Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, Midjourney, and other text-to-image systems rely on written descriptions to generate images using algorithms to convert the text into an image. [7] [8] These system can even produce images according to a specific style like (i.e. photograph, watercolor, illustration, etc.) or artist. [8]
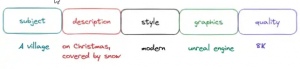
In general, a good prompt for image generation (figure 2) should have in its structure:
- Subject: suggests to the AI model what scene to generate. Represented by nouns.
- Description: additional information related to the subject. Represented by adjectives, background description, or others.
- Style: the theme of the image, which can include artist names or custom styles like fantasy, contemporary, etc.
- Graphics: computer graphics engine type that enforces the efectiveness of the image.
- Quality: quality of the image (e.g. 4K). [1]
While the subject of an intended image, the modifiers— words that describe the style, graphics, and quality—can elevate the quality of the image created. As an example, figure 3 illustrates the most frequently used phrases by Midjourney users. It can be seen that the modifiers are the most used in prompts. [5]
Prompt engineering
Prompt engineering or Prompt design is the practice of discovering the prompt that gets the best result from the AI system. [4] The development of prompts requires human intuition with results that can look arbitrary. [9] Manual prompt engineering is laborious, it may be infeasible in some situations, and the prompt results may vary between various model versions. [3] However, there have been developments in automated prompt generation which rephrases the input, making it more model-friendly. [5]
Text-to-Text
Prompt engineering for text generation
Text-to-Image
Prompt engineering for image generation
Prompt generators

Due to the difficulty of good manual prompt development, several prompt generator models have surfaced (figure 9) that help the user in refining the text input to obtain the best result possible, automatically performing prompt engineering. [3] [5]
- Midjourney Prompt Generator: unofficial Midjourney prompt builder. [10]
- Phraser: assists in creating stronger neural network prompts for Midjourney and DALL-E. [11]
- MidJourney Prompt Helper: text-to-image prompt builder developed for Midjourney and DALL-E. [11]
Drawing Prompt Generator: a prompt helper to aid with artists’ block. [11]
- Promptomania Builder: easy-to-use prompt builder for AI art generators. Works with most CLIP and VQCAN-based models, DALL-E, Midjourney, and others. [11]
- MidJourney Random Commands Generator: unofficial Midjourney prompt generator for complex outputs. [11]
- Lexica.art: a search engine for prompts and artworks. [10]
ChatGPT can also be used to design prompts for AI image generators besides the options above. This can be achieved by asking for adjectives that describe a specific scene (figures 10a and 10b) or directly asking it to write a prompt (e.g. “Write a text prompt for an AI art generation software that would fit the art style of Kilian Eng”). [1] [12]
Security Risks
Prompting vs. Fine-tuning
Prompting and Fine-tuning represent two different ways to leverage large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4.
Fine-tuning involves adapting an LLM's parameters based on a specific dataset, making it a potent tool for complex tasks where accurate, trusted output is vital. However, fine-tuning often requires a labeled dataset and is potentially expensive during the training phase.
Conversely, prompting is the technique of providing specific instructions to an LLM to guide its responses. It doesn't necessitate model retraining for each new prompt or data change, and thus, offers a quicker iterative process. Importantly, it doesn't require a labeled dataset, making it a viable option when training data is scant or absent. Prompting can be an excellent starting point for solving tasks, especially simpler ones, as it can be resource-friendly and computationally efficient.
Despite its advantages, prompting may underperform compared to fine-tuning for complex tasks. There's a clear trade-off in terms of inference costs. Fine-tuned models, by integrating task-specific knowledge into the model's parameters, can generate accurate responses with minimal explicit instructions or prompts, making them cheaper in the long run. In contrast, prompted models, which rely heavily on explicit instructions, can be resource-intensive and more expensive, particularly for large-scale applications. Therefore, the choice between fine-tuning and prompting will depend on the specific use case, data availability, task complexity, and computational resources.
Related Pages
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Ana. B (2022). Design your AI Art generator prompt using ChatGPT. Towards AI. https://pub.towardsai.net/design-your-ai-art-generator-prompt-using-chatgpt-7a3dfddf6f76
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Schmid, S (2022).ChatGPT: How to write the perfect prompts. Neuroflash. https://neuroflash.com/chatgpt-how-to-write-the-perfect-prompts/
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Hao, Y, Chi, Z, Dong, L and Wei, F (2022). Optimizing prompts for text-to-image generation. arXiv:2212.09611v1
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bouchard, L (2022). Prompting explained: How to talk to ChatGPT. Louis Bouchard. https://www.louisbouchard.ai/prompting-explained/
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Turc, J (2022). Crafting prompts for text-to-image models. Towards Data Science. https://towardsdatascience.com/the-future-of-crafting-prompts-for-text-to-image-models-fc7d9614cb65
- ↑ OpenAI (2022). ChatGPT: Optimizing Language Models for dialogue. OpenAI. https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt/
- ↑ Arunk89 (2023). How to write great prompts for AI text-to-image generators. Turbo Future. https://turbofuture.com/internet/How-to-write-great-prompts-for-AI-text-to-image-generator
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 ZMO.AI (2022). How do AI text-to-image generators work? ZMO.AI. https://www.zmo.ai/how-do-ai-text-to-image-generators-work/
- ↑ Pavlichenko, N, Zhdanov, F and Ustalov, D (2022). Best prompts for text-to-image models and how to find them. arXiv:2209.11711v2
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Strikingloo (2022). Stable Diffusion: Prompt guide and examples. Strikingloo. https://strikingloo.github.io/stable-diffusion-vs-dalle-2
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 Yalalov, D (2023). 6 free AI prompt builders and tools that artists actually use in 2023 (Updated). Metaverse Post. https://mpost.io/6-free-prompt-builders-and-helpers-that-artists-actually-use-in-2022/
- ↑ EdXD (2022). Using GPT-3 to generate text prompts for “AI” generated art. ByteXD. https://bytexd.com/using-gpt-3-to-generate-text-prompts-for-ai-generated-art/